SolarProd
Regional Photovoltaic Prediction Tool under Extreme Climate Impact in Hainan
Overview
The project aims to develop a software tool called "SolarProd", which focuses on predicting photovoltaic (PV) power generation systems in the Hainan province under extreme climate conditions. By integrating time-series historical data and graph neural network technology, the tool is capable of providing spatiotemporal predictions of the risks to photovoltaic power generation caused by extreme low-light events.
Methodology
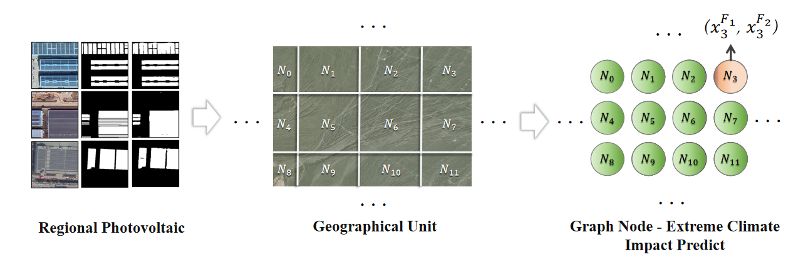
The project involves meteorological data, topographical data, photovoltaic panel data, and expert knowledge closely related to the impact of extreme weather on power grid operation. This integration forms a spatiotemporal knowledge graph for photovoltaic impact analysis based on diverse and heterogeneous spatiotemporal data sources.
When provided with a comprehensive dataset for that region, the tool can analyze and simulate solar radiation, and thus predict the spatiotemporal impact of future extreme weather conditions in that region, particularly extremely low light conditions due to weak solar radiation.
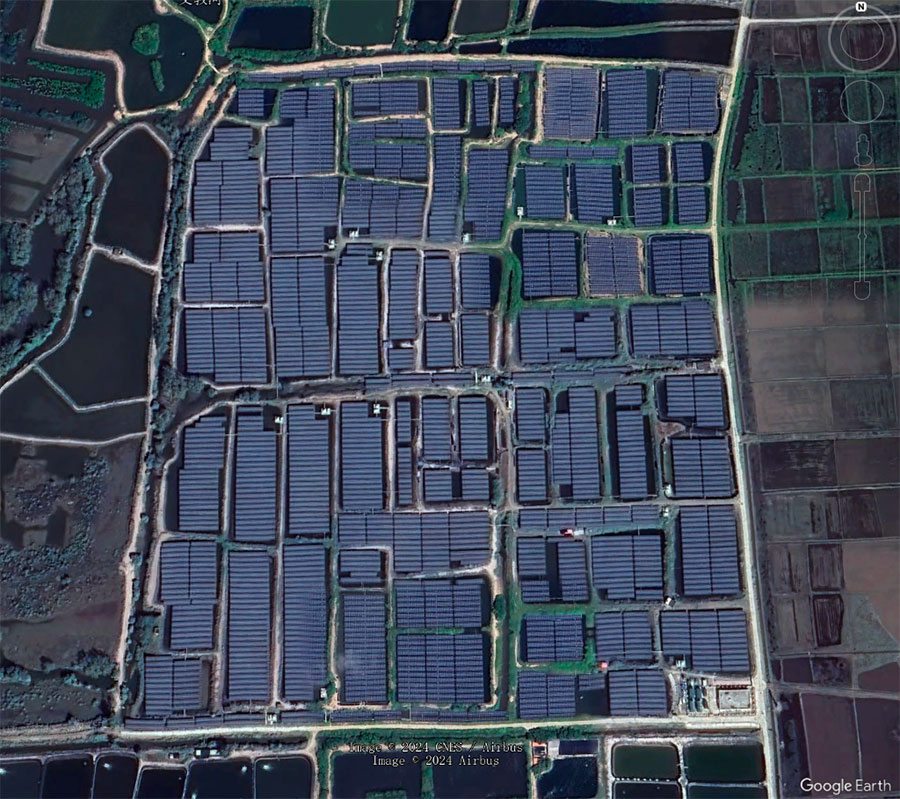
Regional Photovoltaic Prediction Tool under Extreme Climate Impact. © The Aerospace Information Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Application site(s)
Hainan, China
Data
Satellite
- European Space Agency Meteorological Data (Copernicus Climate Data Store)
Other
- Topographical Data (Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center)
- Current Status Data of Photovoltaic Panels
- Photovoltaic Carrier Data
Results - Final product(s)
The SolarProd product is a specialized forecasting tool designed for the photovoltaic power generation systems in specific regions. The expected outcome is that the tool will be able to provide time-series based forecasts, which will display the extremely low light conditions caused by reduced solar radiation during specific time periods, as well as the spatial distribution of the affected photovoltaic panels. These forecasts will be presented in the form of maps and data reports.
Additionally, the tool will provide a sample dataset. The dataset will include time-series solar radiation-related data and photovoltaic panel distribution data for the demonstration area of Hainan province. The solar radiation-related data will be used to train and validate the graph neural network models to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the forecasts.
References
Chen, D.-Y. ; Peng, L. ; Zhang, W.-Y. ; Wang, Y.-D. ; Yang, L.-N. Research on Self-Supervised Building Information Extraction with High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images for Photovoltaic Potential Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5350. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215350