ATTEST
Development of Test Territories to Assess the Sensitivity of Associated Adaptation Strategies
Overview
Despite their very different natures, the feedback between dry periods and local, intense rainfall weakens the soil, a process that amplifies the hazards associated with intense run-off. For example, the formation of a battance crust (a superficial layer of soil that prevents water and air from infiltrating) greatly reduces infiltration capacity and encourages run-off. This crust thus contributes both to erosion in the event of rain and to the non-absorption of useful rainfall, generating periods of water stress combined with periods of drought. Drought, in turn, reduces plant cover and the organic matter content of soils, which erode more easily.
Shortage and excess of water, "Two types of climatic disaster that are really two sides of the same coin, made more frequent and/or more intense throughout France, and sometimes all at once, with alternating droughts and floods in the same areas. It's a new water cycle, one that is sometimes thwarted, and one to which regions must adapt". Jean Jouzel, IPCC 2023
To develop a prevention system designed to reduce the impact of these two hazards, ATTEST is adopting a two-pronged approach:
- Prioritizing intervention sectors,
- Selection of preventive development measures.
Satellite images at different resolutions (metric and sub-metric) coupled with contextual data enable an initial diagnosis to be made and the factors at work to be understood. Once the risk has been established and positioned spatially in the current and future climates (2050 and 2100), local decision-makers need to be able to select preventive measures, and to do this:
- Evaluate the effectiveness of facilities already in place on the ground.
- Understand the different management options that affect land use, local topography and potentially soil type (e.g. types and seasons of crops, hedges, agricultural terraces, hedgerows, buffer zones, contour cultivation, alternating strips, agricultural terraces combined with hedges and infiltration ditches, organic matter, etc.) and consider their effectiveness timeframe (e.g. hedge development time).
- Choose complementary preventive development measures that have proved effective in their context and position them in the area.
- Simulate development scenarios that modify farming practices, local topography and local soil conditions.
- Incorporate these measures into the plans and projects concerned, with implementation dates consistent with the risks assessed.
|
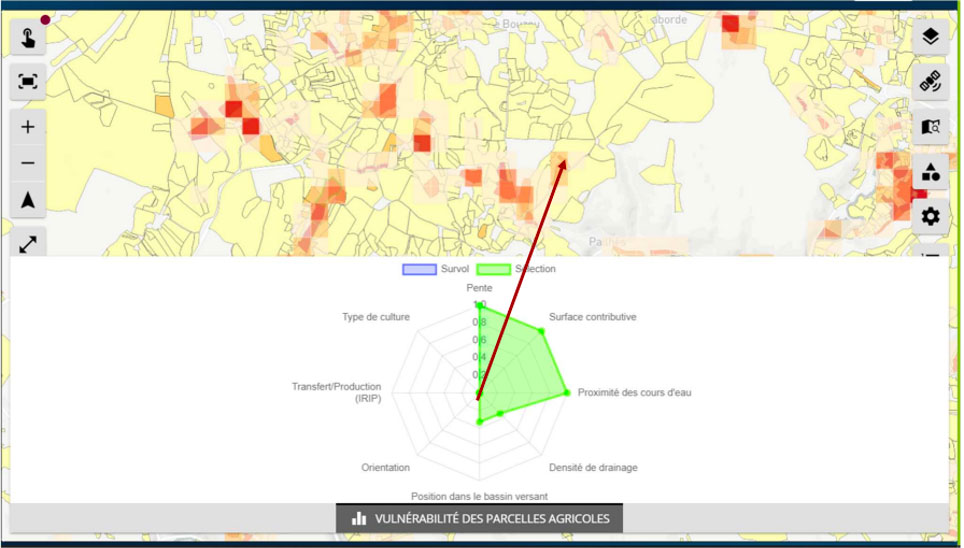
The FORO (Flood Observatory for Resilient Occitanie) platform developed by SCO FLAude can already be used to pinpoint areas of vulnerability to intense runoff in a given region and identify possible measures. The objectives of ATTEST go beyond diagnosis and understanding of the phenomena at work to include decision support and evaluation of the procedures adopted in the regions. |
FORO screen copy - Multi-criteria vulnerability rating using the IRIP method (INRAE) for a selected 100mx100m tile, which will be supplemented by climate projections as part of the ATTEST project. © SGEvT |
Application site(s)
France :
-
Pas-de-Calais Department, 66 municipalities
👉 The user partner is SmageAa (Syndicat Mixte pour l'Aménagement et la Gestion des Eaux de l'Aa / Mixed Syndicate for the Development and Management of Aa Waters) -
Aude Department, 436 municipalities
👉 The user partner is the EPTB (Public Territorial Basin Establishment) SMMAR AUDE (Syndicat Mixte des Milieux Aquatiques et des Rivières de l'Aude / Aude joint association for aquatic environments and rivers). -
Data
Satellite
Spatial imagery is used in a scalar approach covering resolutions ranging from decametric to sub-metric in relation to the actions to be carried out. Thus:
-
Sentinel-2 data are used to understand how a watershed functions, and the various management levers that can be activated. Given their temporal depth and the areas covered, they are ideally suited to assessing issues at a global level.
-
The implementation of specific planning measures, and above all the evaluation of their effectiveness, notably through the detection of local changes, requires a higher resolution, which falls within the sub-metric domain. In this respect, Pleiades imagery is ideally suited to evaluative measures. Archival images are required, and specific acquisition may be requested in the event of an intense event.
Other
The methods used, particularly in determining runoff zones (IRIP), call on various digital sources. These include DTMs, IGN reference systems (BD TOPO in particular), crop information (RPG) and meteorological data derived from climate observation and modelling.
Results – Final product(s)
The final products can be broken down into two types of service:
- Operational decision support services including:
- A scoring tool integrating current and future climate to prioritize actions to be taken.
- A tool for automated generation of prevention scenarios incorporating preventive layout simulations.
- A multi-factor cost/benefit analysis tool to rank preventive development scenarios according to their reduction effect, to be re-evaluated according to local constraints.
- A protocol for handling requests from local players to help them select development strategies, with support services provided by partner consultancies.
- Development effectiveness verification services including:
- The commissioning of an algorithm for detecting runoff-related damage following an extreme climatic event by comparing Sentinel-2 before/after satellite images (industrialization of the SPCD comparison model already developed by INRAE/ONERA (Cerbalaud & al., 2022; 2023)).
- The development of a tool to measure the effectiveness of the schemes implemented and tested, based on the experience of the 2 partner areas.
References
- Sébastien Le Corre, Gwendoline Blanchet et al, Résilience et adaptation des territoires aux changements climatiques exemple de la gestion du ruissellement en espace rural dans l’Aude 35ème colloque annuel de l’Association Internationale de Climatologie – AIC 2022.
- Cerbelaud, A.; Blanchet, G.; Roupioz, L.; Breil, P.; Briottet, X. Mapping Pluvial Flood-Induced Damages with Multi-Sensor Optical Remote Sensing: A Transferable Approach. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2361.
- Cerbelaud, A.; Breil, P.; Blanchet, G.; Roupioz, L.; Briottet, X. Proxy Data of Surface Water Floods in Rural Areas: Application to the Evaluation of the IRIP Intense Runoff Mapping Method Based on Satellite Remote Sensing and Rainfall Radar. Water 2022, 14, 393.
Related project(s)
SCO FLAude and its FORO platform, which enables rural stakeholders to visualise and better understand the risks associated with flash floods in order to implement resilience plans.
SCO ASGARD, Satellite data assimilation to ensure prevention and early warning of rainwater runoff and associated disasters
Project news
🎥 03/12/2025: Presentation of the ATTEST project and its progress at the 19th Quarterly Meeting of SCO France